Cogeneration / Combined Heat and Power CHP
Cogeneration also known as combined heat and power (CHP) is the simultaneous production of electricity with the recovery and utilisation of the heat generated. Cogeneration is a highly efficient form of energy conversion and it can achieve primary energy savings of approximately 40% by compared to the separate purchase of electricity from the national electricity grid and a gas boiler for onsite heating. Combined heat and power plants are typically embedded close to the end user and therefore help reduce transportation and distribution losses, improving the overall performance of the electricity transmission and distribution network.
Green Power offers fully engineered combined heat and power generators, engines and other solutions, which provide a clean, efficient and reliable approach to generating power and thermal energy from a single fuel source. Combined heat and power systems offer considerable environmental benefits when compared with purchased electricity and onsite-generated heat.
By utilizing the heat byproduct of electricity generation, JINAN CHP generators can be designed to meet the thermal and electrical base loads of a facility. JINAN CHP systems are integrated so that waste heat is recovered and used for heating, cooling, dehumidification and other processing applications. This advanced technology decreases energy costs and increases efficiency by up to 90%. Less fuel needs to be consumed to generate the same amount of energy, resulting in fewer emissions.
We have the experience and capability to engineer the right JINAN CHP engine to meet your requirements; we provide sizing and evaluation of your electrical load profile and assessment of your heat demand.
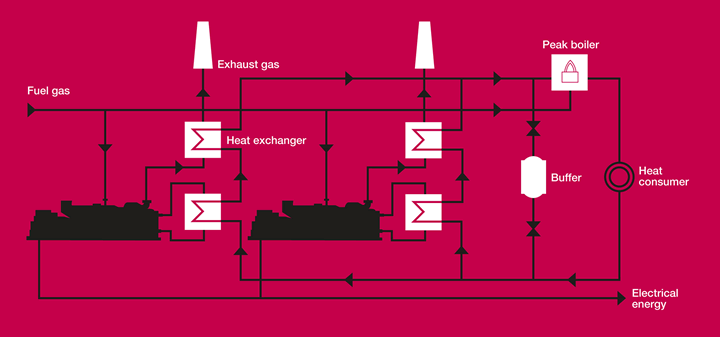
Heat Sources from a Gas Engine
The heat from the generator is available from five (5) key areas:
- Engine jacket cooling water
- Engine lubrication oil cooling
- First stage air intake intercooler
- Engine exhaust gases
- Engine generator radiated heat, second stage intercooler
1, 2 and 3 are recoverable in the form of hot water, typically on a 70/90˚C flow return basis and can be interfaced with the site at a plate heat exchanger.The engine exhaust gases typically leave the engine at between 400 and 500˚C. This can be used directly for drying, in a waste heat boiler to generate steam, or through an exhaust gas heat exchanger combining with the heat from the cooling circuits. The heat from the second stage intercooler is also available for recovery as a lower grade heat.
CHP applications
We provide JINAN CHP generators and engines for use in any of the following applications:
- Manufacturing facilities including pulp and paper processing, food processing, refining and other industrial processes.
- Education, healthcare and military institutions.
- Large office and other commercial buildings including hotels, airports, malls and more.
- Municipal power generation, wastewater treatment and other facilities.
Benefits of Gas Engine CHP
The high efficiency of a CHP plant compared with conventional bought-in electricity and site-produced heat provides a number of benefits including
• Completely engineered solutions from extensive power generation experience
• Reduced energy costs
• Lower emissions
• Excellent reliability
• Flexibility in support, application, engineering and design
• Modular components, supporting ease of installation and reliable operation
• Increased security and power quality, protecting your revenue stream
• After sales support, service and performance guarantees of your CHP asset.